Transition metal boryl complex
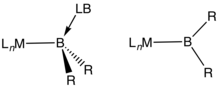
In chemistry, a transition metal boryl complex is a molecular species with a formally anionic boron center coordinated to a transition metal.[1] They have the formula LnM-BR2 or LnM-(BR2LB) (L = ligand, R = H, organic substituent, LB = Lewis base). One example is (C5Me5)Mn(CO)2(BH2PMe3) (Me = methyl).[2] Such compounds, especially those derived from catecholborane and the related pinacolborane, are intermediates in transition metal-catalyzed borylation reactions.
Synthesis
[edit]Oxidative addition is the main route to metal boryl complexes. Both B-H and B-B bonds add to low-valent metal complexes. For example, catecholborane oxidatively adds to Pt(0) to give the boryl hydride.[4]
- C6H4O2BH + Pt(PR3)2 → C6H4O2B Pt(PR3)2H
Addition of diboron tetrafluoride to Vaska's complex gives the triboryl iridium(III) derivative:
- 2 B2F4 + IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2 → Ir(BF2)3(CO)(PPh3)2 + ClBF2
References
[edit]- ^ Geoffrey J. Irvine; M. J. Gerald Lesley; Todd B. Marder; Nicholas C. Norman; Craig R. Rice; Edward G. Robins; Warren R. Roper; George R. Whittell; L. James Wright (1998). "Transition Metal−Boryl Compounds: Synthesis, Reactivity, and Structure". Chem. Rev. 98 (8): 2685–2722. doi:10.1021/cr9500085. PMID 11848976.
- ^ Staubitz, A.; Robertson, A. P. M.; Sloan, M. E.; Manners, I. (2010). "Amine− and Phosphine−Borane Adducts: New Interest in Old Molecules". Chem. Rev. 110 (7): 4023–4078. doi:10.1021/cr100105a. PMID 20672859.
- ^ C.Borner; K.Brandhorst; C.Kleeberg (2015). "Selective B–B bond activation in an unsymmetrical diborane(4) by [(Me3P)4Rh–X] (X = Me, OtBu): a switch of mechanism?". Dalton Trans. 44 (18): 8600–8604. doi:10.1039/C5DT00618J. PMID 25868980.
- ^ Neeve, Emily C.; Geier, Stephen J.; Mkhalid, Ibraheem A. I.; Westcott, Stephen A.; Marder, Todd B. (2016). "Diboron(4) Compounds: From Structural Curiosity to Synthetic Workhorse". Chemical Reviews. 116 (16): 9091–9161. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00193. hdl:1807/78811. PMID 27434758.
